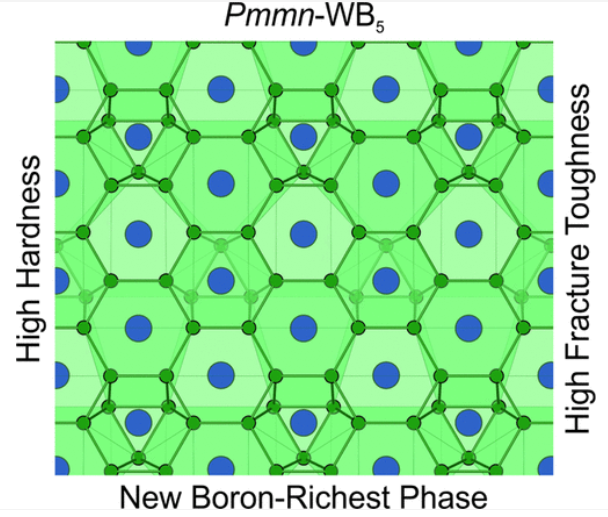
Computational Search for Super-hard materials.
Superhard materials play a pivotal role in numerous applications, defined by a Vickers hardness surpassing 40 GPa. Among the well-known superhard materials are various carbon allotropes, with diamond ranking as the hardest material. This is closely followed by carbon nitrides, cubic boron nitride, and diverse boron allotropes. Transition metal compounds such as chromium, rhenium, molybdenum, and tungsten in the form of borides, nitrides, and carbides also exhibit exceptional hardness, with tungsten carbide (WC) and titanium nitride (TiN) being widely used in machining tools and mining equipment. Our research endeavors to discover novel binary, ternary, and quaternary superhard materials within the categories of carbides, borides, and nitrides. By expanding our understanding of these materials, we aim to contribute to the development of new superhard compounds with potential applications across various industries.